EP 1110-2-12
30 Sep 95
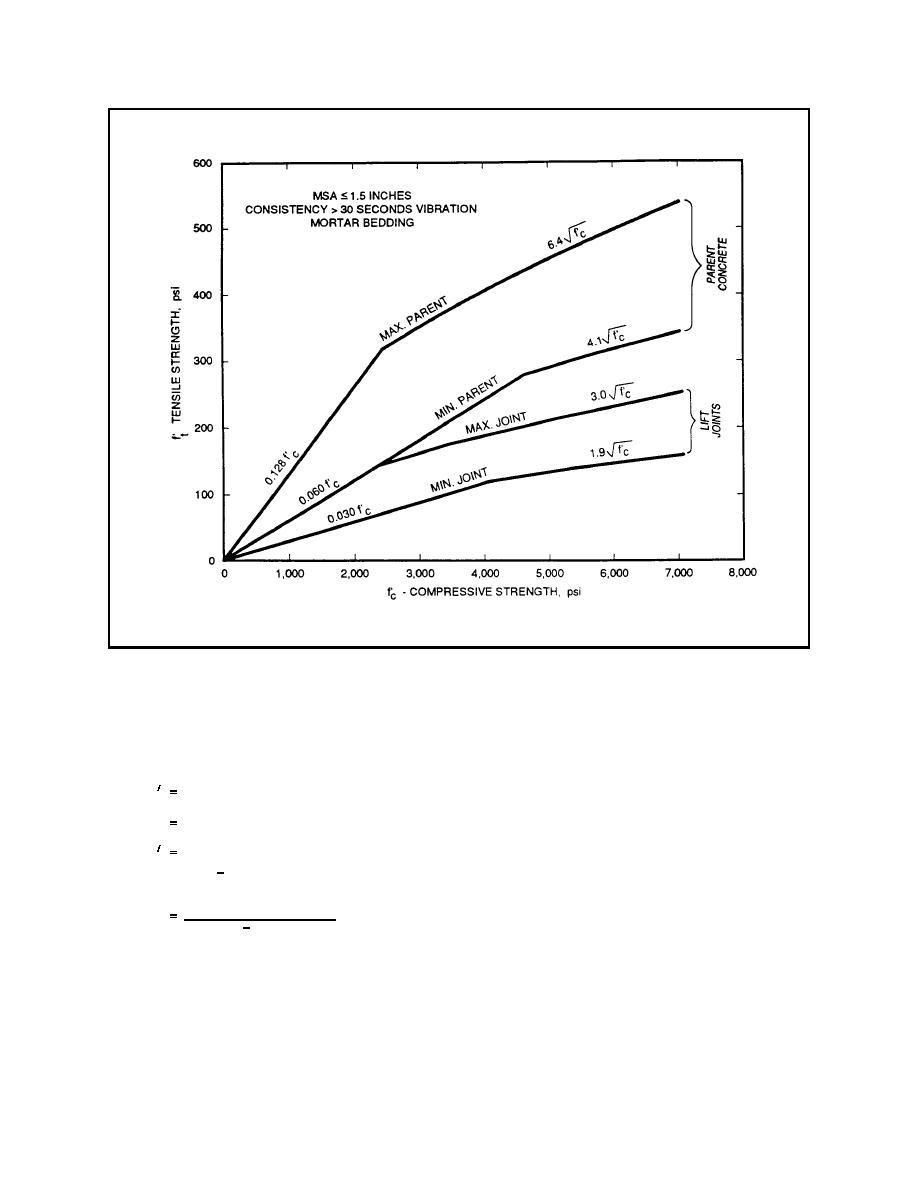
Figure 3-3. Tensile strength range, RCC, MSA ≤ 1.5 inches, consistency > 30 seconds vibration, mortar
bedding
ulus of elasticity calculated by the above formula
The relationship between strain rate and modulus of
elasticity is as follows (Bruhwieler 1990):
(Dunstan 1978). The modulus of elasticity may
exhibit some anisotropic behavior due to the coarse
aggregate particle alignment as discussed in
E(Er)0.020
E
paragraph 3-3d(2); however, the effects on the
modulus will be small and can be disregarded when
where E
static modulus of elasticity
performing a dynamic stress analysis.
E
seismic modulus of elasticity at the
quasi static rate
3-6.
Poisson's Ratio
high seismic strain rate
Er
Poisson's ratio for RCC is the same as for conven-
quasi static rate
tional mass concrete. For static loads, values range
between 0.17 and 0.22, with 0.20 recommended when
For a seismic strain rate equal to 1,000 times the
testing has not been performed. Poisson's ratio is also
quasi-static rate the seismic modulus of elasticity is
strain rate sensitive, and the static value should be
1.15 times the static modulus. For long-term load-
reduced by 30 percent when evaluating stresses due
ings where creep effects are important, the effective
to seismic loads (Bruhwieler 1990).
modulus of elasticity may be only 2/3 the static mod-
3-4



 Previous Page
Previous Page
