SECTION FIVE
Performance Standards and Construction Quality Control
As discussed previously, perimeter air monitoring was routinely performed at the site. Three
VOCs were selected as key indicator compounds to be monitored by the HNu if the average
NMOC reading exceeded 1 parts per million (ppm). Perimeter action levels were set at 10% of
the OSHA permissible exposure limits (PELs) for each of the three selected contaminants. The
perimeter action levels were:
9.146 ppm for toluene
7.777 ppm for chlorobenzene
2.511 ppm for tetrachloroethene
The table below provides the discharge limitations for the WWTP at the SCS Site as specified in
the September 1988 ROD. Weekly samples of the WWTP effluent were required whenever the
WWTP was in operation.
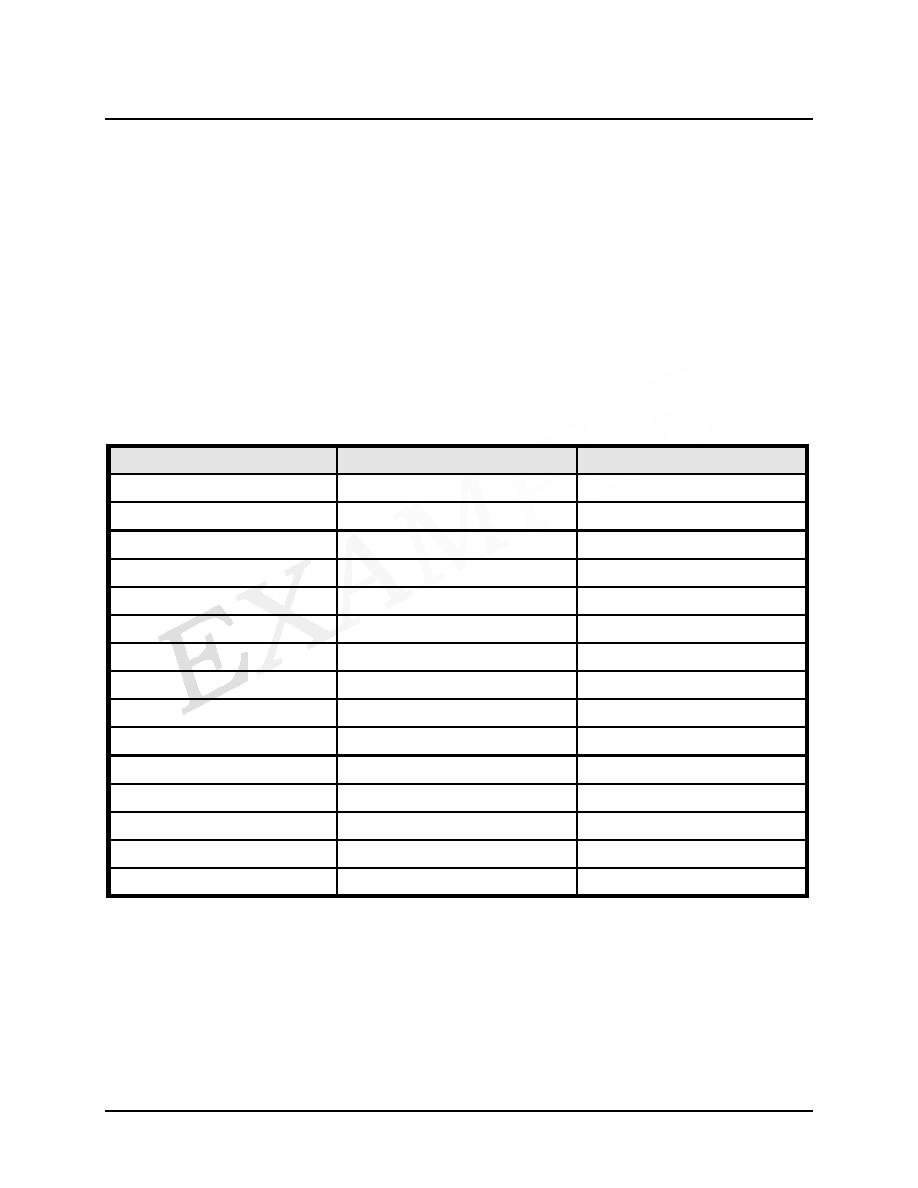
Wastewater Discharge Limitations
Parameter
Monthly Average (mg/L)
Daily Maximum (mg/L)
β-Naphthylamine
0.012
0.024
Fenac
0.100
0.200
Toluene
0.010
0.020
Chlorobenzene
0.010
0.020
1,2-Dichlorobenzene
0.010
0.020
1,4-Dichlorobenzene
0.010
0.020
1,2-Dichloroethane
0.010
0.020
Trichloroethene
0.005
0.010
Total Arsenic
0.100
0.200
Total Barium
2.000
4.000
Total Cadmium
0.060
0.120
Total Nickel
0.200
0.400
Total Chromium
0.150
0.300
Total Lead
1.000
2.000
pH
6 to 9 standard units
6 to 9 standard units
QUALITY ASSURANCE AND QUALITY CONTROL
Data Assessment
An incineration feasibility study was conducted between October 1990 and August 1991. All test
runs met the cleanup criteria established for the SCS Site. The pilot-scale rotary kiln incinerator
achieved 99.99% destruction removal efficiency (DRE) of Principal Organic Hazardous
Constituents (POHCs), which were spiked into the soil. The leachable metal concentrations in
5-2
Slippery Chemical OU 3 Final RA Report



 Previous Page
Previous Page
