EP 1110-2-12
30 Sep 95
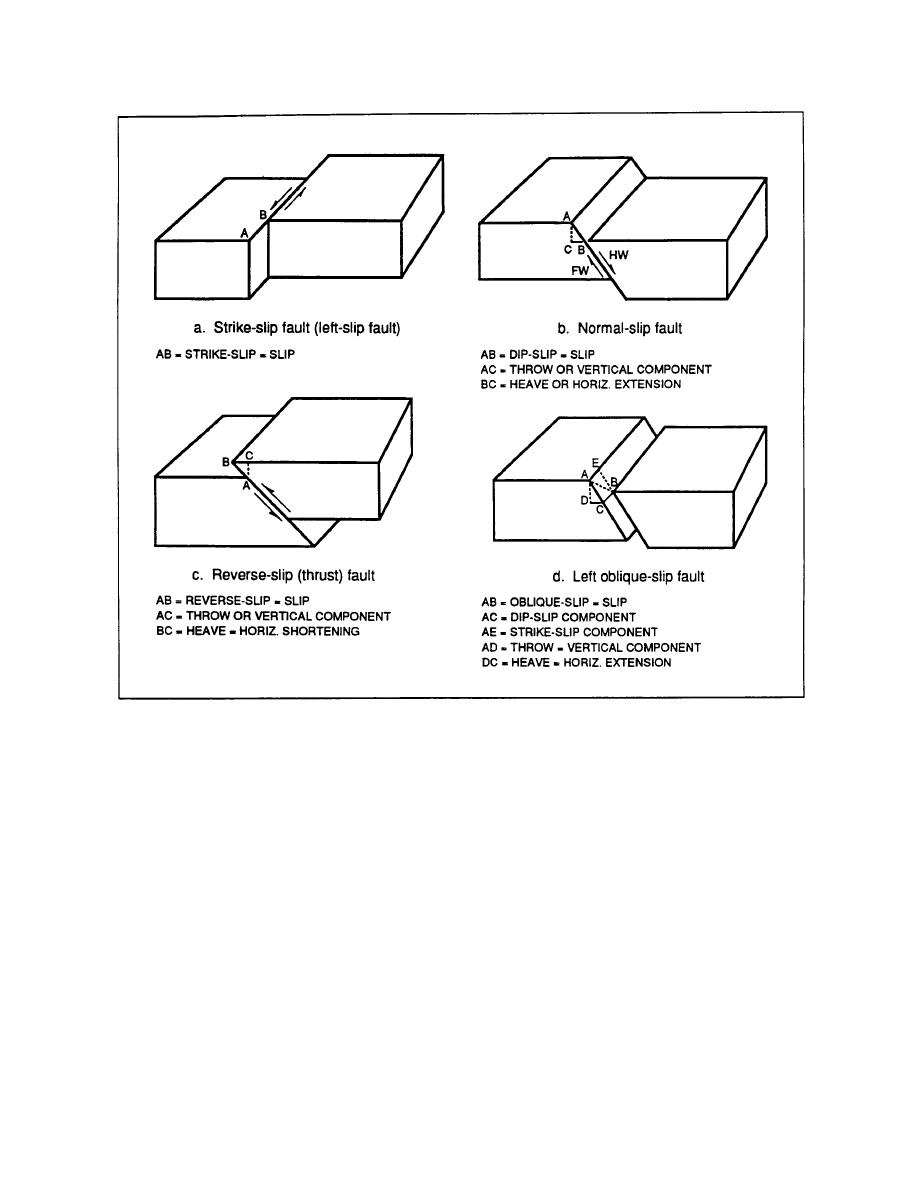
Figure 2-1. Types of fault slips
ment. Stresses due to ground shaking are determined
unusual causes of foundation fault displacement
by methods discussed earlier in this chapter. Thus,
discussed later in this chapter. In these situations the
stresses due to fault displacement and stresses due to
strong motion shaking accompanying the local fault
ground shaking are obtained from two separate, inde-
slip may be nearly as intense or even more intense
pendent, and approximate analyses. The response to
than the gound motion shaking associated with an
the design earthquake is then obtained by direct addi-
OBE produced by a major active fault slip occurring
tion of the two sets of stresses without accounting for
some distance from the site. When this is the case, a
any interaction. Actually, the fault displacement may
reduced value of the DFD would be included with
cause inelastic behavior at the dam-foundation inter-
free field ground motion to describe the OBE.
face, cracking within the RCC, or other inelastic
response which changes the dynamic characteristics
d. Combined DFD and ground shaking.
of the dam, which in turn interacts with and effects
Stresses associated with the DFD result from highly
the ground shaking response. Because these simpli-
complex nonlinear behavior; however, simplified fault
fied and approximate procedures have not been sup-
displacement analysis procedures, such as the one
ported by nonlinear finite element analyses that
described below, are normally used to investigate
properly combine the effects of fault displacement
concrete stresses that may occur due to fault displace-
2-3



 Previous Page
Previous Page
