EP 1110-1-27
27 Jan 00
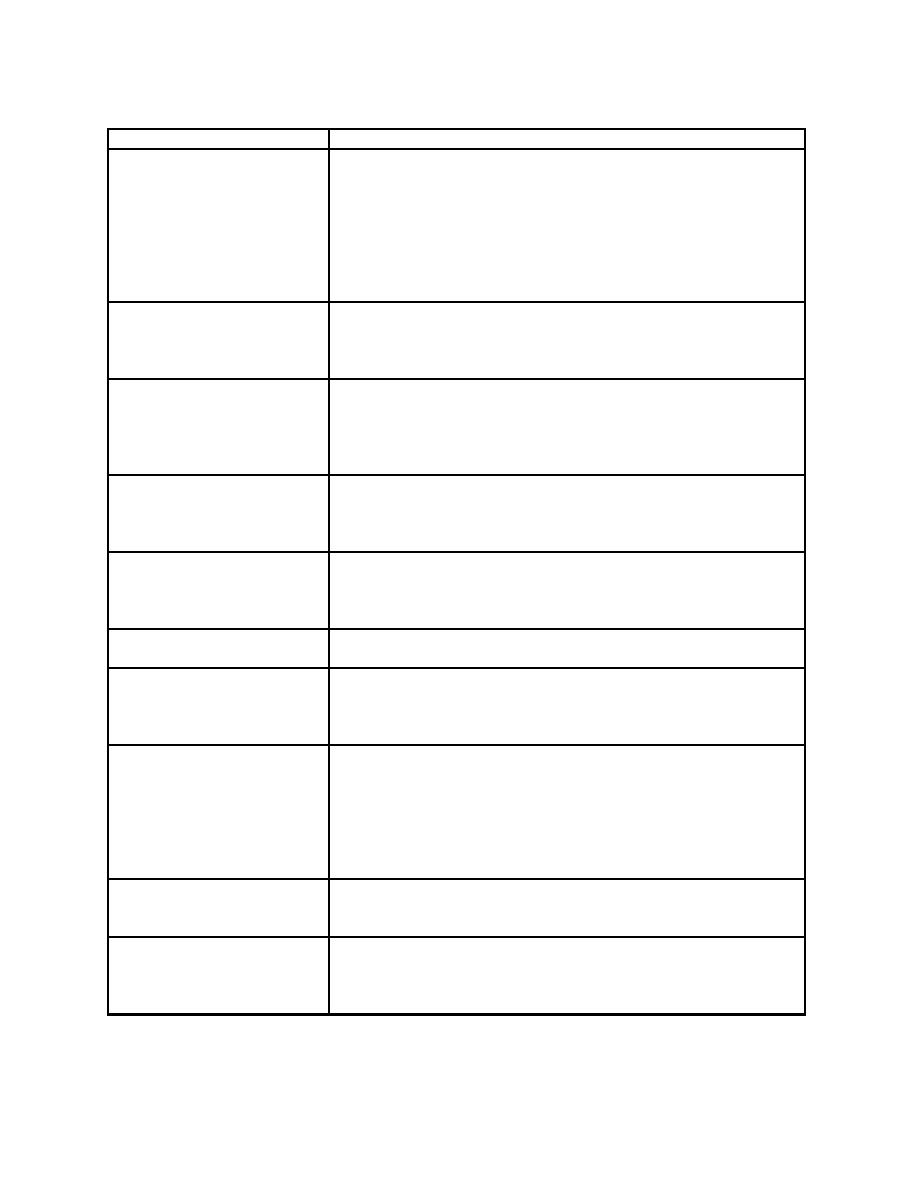
Table 2-1. Definitions of Poor Well Performance and Causes
Problems
Causes
Sand/Silt Pumping: Pump and
Inadequate screen and filter-pack selection or installation, incomplete
equipment wear and plugging.
development, screen corrosion, collapse of filter pack due to washout
resulting from excessive vertical velocity in the filter pack, presence
of sand or silt in fractures intercepted by a well completed "open-
hole," incomplete casing bottom seat (casing-screen break) or
casing-screen break due to settlement, ground movement, or poor
installation. Pumping in excess of gravel pack and system capacity
(oversized pump, pipe breakage lowering pumping head, etc.).
Silt/Clay Infiltration: Filter
Inadequate well casing seals, infiltration through filter pack, or "mud
clogging, sample turbidity.
seams" in rock, inadequate development, or casing-screen break due
to settlement, ground movement, or poor installation. Formation
material may be so fine that engineered solutions are inadequate.
Pumping Water Level
Area or regional water-level declines, pumping in excess of
Decline: Reduced yields,
sustainable well capacity, well interference, or well plugging or
increased oxidation, well
encrustation. Sometimes a regional decline will be exaggerated at a
interference, impaired pump
well due to plugging.
performance.
Injection water level rise and
Area or regional water-level rise; injection in excess of sustainable
reduced acceptance rate or
well capacity; well plugging or encrustation; encrustation, plugging,
increased injection system
or corrosion and perforation of discharge lines; increased TDH in
head.
water delivery system.
Lower (or Insufficient) Yield:
Dewatering or caving in of a major water-bearing zone, pump wear
Unsatisfactory system
or malfunction, encrustation, plugging, or corrosion and perforation
performance.
of discharge lines, increased total dynamic head (TDH) in water
delivery or treatment system.
Complete Loss of Production:
Most typically pump failure. Also loss of well production due to
Failure of system.
dewatering, plugging, or collapse.
Chemical Encrustation:
Deposition of saturated dissolved solids, usually high Ca, Mg
Increased drawdown, reduced
carbonate, and sulfate salts or iron oxides, or FeII sulfides. May
output or reduced injection
occur at chemical feed points, e.g., feeding caustic soda to raise pH
acceptance rate.
into a Ca-rich water.
Biofouling Plugging:
Microbial oxidation and precipitation of Fe, Mn, and S (sometimes
Increased drawdown, reduced
other redox-changing metals that are low solubility when oxidized)
output or reduced injection
with associated growth and slime production. Often associated with
acceptance rate, alteration of
simultaneous chemical encrustation and corrosion. Associated
samples, clogging of filters
problem: well "filter effect": samples and pumped water are not
and lines.
necessarily representative of the aquifer. Often works simultaneously
with other problems such as silting.
Pump/Well Corrosion: Loss
Natural aggressive water quality, including H2S, NaCl-type waters,
of performance, sanding, or
biofouling and electrolysis due to stray currents. Aggravated by poor
turbidity.
engineered material selection.
Well Structural Failure: Well
Tectonic ground shifting, ground subsidence, failure of unsupported
loss and abandonment.
casing in caves or unstable rock due to poor grout support, casing or
screen corrosion and collapse, casing insufficient, local site
operations.
2-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
